Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsuchida, Daiki; Konda, Miki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-002, 81 Pages, 2023/05
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-004, 87 Pages, 2022/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until by the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed samples generated from JPDR, JRR-3 and JRR-4. In this report, radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) were determined based on radiochemical analysis and summarized as basic data for the study of evaluation method of radioactive concentration.
Cm) were determined based on radiochemical analysis and summarized as basic data for the study of evaluation method of radioactive concentration.
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-006, 70 Pages, 2020/08
Radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried at the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JPDR and JRR-4. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Hayashi, Takao; Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Ikeda, Kazuki*; Nakamori, Yuko*; Orimo, Shinichi*; DEMO Plant Design Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1285 - 1290, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:78.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron transport calculations were carried out to evaluate the capability of metal hydrides and borohydrides as an advanced shielding material. Some hydrides indicated considerably higher hydrogen content than polyethylene and solid hydrogen. The hydrogen-rich hydrides show superior neutron shielding capability to the conventional materials. From the temperature dependence of dissociation pressure, ZrH and TiH
and TiH can be used without releasing hydrogen at the temperature of less than 640
can be used without releasing hydrogen at the temperature of less than 640  C at 1 atm. ZrH
C at 1 atm. ZrH and Mg(BH
and Mg(BH )
) can reduce the thickness of the shield by 30% and 20% compared to a combination of steel and water, respectively. Mixing some hydrides with F82H produces considerable effects in
can reduce the thickness of the shield by 30% and 20% compared to a combination of steel and water, respectively. Mixing some hydrides with F82H produces considerable effects in  -ray shielding. The neutron and
-ray shielding. The neutron and  -ray shielding capabilities decrease in order of ZrH
-ray shielding capabilities decrease in order of ZrH
 Mg(BH
Mg(BH )
) and F82H
and F82H  TiH
TiH and F82H
and F82H  water and F82H.
water and F82H.
Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio
Bunseki Kagaku, 55(1), p.51 - 54, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.45(Chemistry, Analytical)A relatively large quantity of sample solutions have to be prepared for radiochemical analysis of solidified products yielded by plasma melting treatment of non-metallic radioactive wastes. In order to dissolve the solidified products sample rapidly, dissolution method with microwave heating devices was applied. In a conventional method only by external heating with various mixtures of acids (HNO , HF, HClO
, HF, HClO and H
and H SO
SO ), a 0.1 g amount of the sample was dissolved with difficulty. However, applying the microwave assisted dissolution method, a 1 g amount of the sample was completely dissolved in a shorter time. Thereby the time for dissolution procedures was shortened less than a one-tenth. The present dissolution method was successfully applied to the blast furnace slag as a reference material to determine main elements with good precision.
), a 0.1 g amount of the sample was dissolved with difficulty. However, applying the microwave assisted dissolution method, a 1 g amount of the sample was completely dissolved in a shorter time. Thereby the time for dissolution procedures was shortened less than a one-tenth. The present dissolution method was successfully applied to the blast furnace slag as a reference material to determine main elements with good precision.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(2), p.127 - 134, 2005/06
The fractional distillation characteristics of the materials used for the reactor pressure vessel made of ASTM A302B and the structures in reactor made of SUS304 which are the radioactive metallic waste of Japan Power Demonstration Reactor (JPDR) were analyzed numerically. In the simulation, the vaporization rates of the components of the waste were calculated by using the Langmuir's equation and Henry's law. As the result of simulation, it was calculated that  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  C and
C and  Nb can be reduced to less than clearance level by the fractional distillation. On the ASTM A302B case, it was pointed out that the other radioactive nuclei which are
Nb can be reduced to less than clearance level by the fractional distillation. On the ASTM A302B case, it was pointed out that the other radioactive nuclei which are  Mn,
Mn,  Fe,
Fe,  Co,
Co,  Ni and
Ni and  Ni satisfy clearance level after 77 years cooling down. On the SUS304 case, it was pointed out that
Ni satisfy clearance level after 77 years cooling down. On the SUS304 case, it was pointed out that  Ni and
Ni and  Ni must be separated to satisfy clearance level using isotope separation.
Ni must be separated to satisfy clearance level using isotope separation.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
RIST News, (39), p.23 - 31, 2005/03
For the separation of radionuclide from the radioactive metallic waste generated by the decommissioning of nuclear facilities, a new method combined with the distillation and laser separation is being studied. The characteristics of fractional distillation for duralumin were analyzed numerically using the Henry's law and the Langmuir's equation, and its result agreed well with the experiment. Next, the fractional distillation characteristics of the materials used for the structures in reactor made of SUS304 which are the radioactive metallic waste of Japan Power Demonstration Reactor (JPDR) were analyzed numerically. As the result of the simulation, it was calculated that the radioactive metallic waste will be reduced to less than 1/100.
Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Hirabayashi, Takakuni*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(9), p.919 - 924, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new laser decontamination method utilizing a gel made from a sodium silicate solution and an acid was developed for removing radioactive nuclide incorporated into a surface oxide layer on metal waste. Decontamination tests were carried out using both simulated contaminated samples and pipe specimens cut from the primary coolant system of the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor. In the case of surface oxide layer consisting mainly of iron oxide, more than 99% of surface radioactivities were removed after two to three decontamination runs. In order to ascertain the role of laser irradiation on chemical reactions, chemical states of O and Fe in the oxide layer before and after decontamination were analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. It was found that the oxide layer was dissolved into the acid-containing gel, and the reaction was extensively promoted by the laser irradiation.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
JAERI-Research 2004-012, 12 Pages, 2004/08
The fractional distillation characteristics at between 0  C and 2500
C and 2500  C(the rate is 200
C(the rate is 200  C/h) of radioactive metallic waste for JPDR which mainly consists of stainless steel were analyzed numerically. In the simulation, the vaporization rates of the components of JPDR waste were calculated by using the Langmuir's equation and Henry's law. As the results, it was calculated that
C/h) of radioactive metallic waste for JPDR which mainly consists of stainless steel were analyzed numerically. In the simulation, the vaporization rates of the components of JPDR waste were calculated by using the Langmuir's equation and Henry's law. As the results, it was calculated that 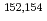 Eu,
Eu,  C and
C and  Nb can be removed by the fractional distillation. On the other hand,
Nb can be removed by the fractional distillation. On the other hand,  Mn and
Mn and  Fe can be reduced by cooling them for about 30 years. Therefore, by removing
Fe can be reduced by cooling them for about 30 years. Therefore, by removing  Ni and
Ni and  Co using laser separation method, it will be possible to reduce the radioactive metallic waste by less than one one-hundredth.
Co using laser separation method, it will be possible to reduce the radioactive metallic waste by less than one one-hundredth.
Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao*; Tobita, Hiroshi; Mori, Takamasa
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(2), p.185 - 192, 2004/06
no abstracts in English
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
JAERI-Research 2003-022, 16 Pages, 2003/10
We measured and simulated the characteristics of vacuum distillation for duralumin (Aluminum alloy 7075: Al-5.6Zn-2.5Mg-1.6Cu-0.25Cr). In the experiment, the duralumin (378.7 mg) was heated to 1500 C (the rate is 200
C (the rate is 200 C/hour) and vaporized. The ion current of components within the vapor using mass spectrometer was measured. In the simulation, the vaporization rate of components within vapor was calculated by using the formula of Langmuir and the law of Raoult. The simulation agreed well with the experiment, and it was found that the group of Al, Cu and Cr, and the group of Mg and Zn could be separated by the vacuum distillation.These results show that the radioactive wastes can be reduced using the vacuum distillation.
C/hour) and vaporized. The ion current of components within the vapor using mass spectrometer was measured. In the simulation, the vaporization rate of components within vapor was calculated by using the formula of Langmuir and the law of Raoult. The simulation agreed well with the experiment, and it was found that the group of Al, Cu and Cr, and the group of Mg and Zn could be separated by the vacuum distillation.These results show that the radioactive wastes can be reduced using the vacuum distillation.
Nakamura, Hisashi; Hirabayashi, Takakuni; Akimoto, Jun*; Takahashi, Kenji*; Shindo, Hideaki; Sakurai, Daihachiro*; Almansour, A.*; Okane, Toshimitsu*; Umeda, Takateru*
Materials Science Forum, 329-330, p.441 - 448, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hisashi; Hirabayashi, Takakuni
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-6-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu '98 Koen Rombunshu, p.371 - 376, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Kameo, Yutaka; Aoki, Kazuhiro; ; Hirabayashi, Takakuni
Proc. of 1998 JAIF Int. Conf. on Water Chemistry in Nucl. Power Plants (Water Chemistry'98), p.571 - 574, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hisashi; Fujiki, Kazuo
Nuclear Technology, 117(2), p.195 - 205, 1997/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hisashi; Kanazawa, Katsuo; Sato, Takayuki; ; Fujiki, Kazuo
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (9), p.41 - 50, 1993/12
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hisashi; Fujiki, Kazuo
Technology and Programs for Radioactive Waste Management and Environmental Restoration,Vol. 2, p.1683 - 1686, 1993/00
no abstracts in English
Kobutsugaku Zasshi, 19(5), p.289 - 293, 1990/07
no abstracts in English
Suwa, Takeshi; ; *
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (2), p.29 - 40, 1990/00
no abstracts in English